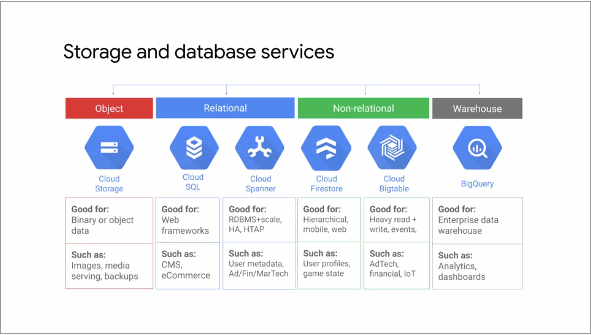
So you’ve got a ton of data that needs to be stored and managed efficiently? Look no further than GCP Firestore. This powerful NoSQL database offered by Google Cloud Platform is designed to handle your scaling needs with ease. Whether you’re dealing with large amounts of data or expecting rapid growth, Firestore has got you covered. With its flexible data model, automatic scaling, and powerful querying capabilities, this scalable database solution is a game-changer for businesses of all sizes. Say goodbye to worrying about capacity limits and slow performance, and say hello to seamless scalability with GCP Firestore.
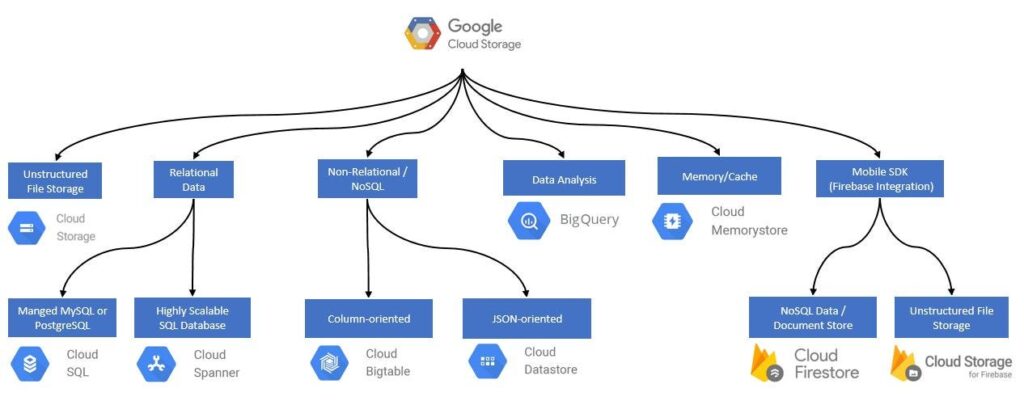
Overview of GCP Firestore
What is GCP Firestore?
GCP Firestore is a scalable NoSQL database offered by Google Cloud Platform (GCP) that allows you to store, manage, and query your data in a flexible and efficient manner. It is a document-oriented database that enables you to store data in a hierarchical structure, making it easy to organize and retrieve information.
Key features of GCP Firestore
GCP Firestore offers a range of key features that make it a powerful and versatile NoSQL database. These features include:
-
Scalability: GCP Firestore is designed to handle large amounts of data and high loads. It can automatically scale to accommodate increased traffic and storage requirements, allowing your application to grow seamlessly.
-
Real-time updates: GCP Firestore provides real-time data synchronization, meaning that any changes made to the database are immediately propagated to all connected devices or clients. This enables you to build real-time collaborative applications or synchronize data across multiple devices.
-
Strong consistency: GCP Firestore ensures that all read and write operations are strongly consistent, meaning that any changes made to the database are immediately visible to subsequent read operations. This guarantees data integrity and ensures that your application always sees the latest state of the data.
-
Querying and indexing: GCP Firestore supports powerful querying capabilities, allowing you to retrieve data based on specific criteria. It also provides automatic indexing of all fields, making queries fast and efficient.
-
Security and access control: GCP Firestore allows you to define fine-grained access control policies, ensuring that only authorized users or applications can access and modify your data. It integrates with GCP Identity and Access Management (IAM) for easy management of access rights.
Benefits of using GCP Firestore
Using GCP Firestore offers several benefits for your data management needs. These include:
-
Scalability: GCP Firestore’s ability to scale automatically allows your application to handle increased traffic and data storage without any manual intervention. This ensures that your application remains performant and responsive as your user base grows.
-
Real-time collaboration: With GCP Firestore, you can easily build applications that support real-time collaboration and synchronization. This is particularly useful for applications such as collaborative document editing, real-time chat, or multi-player games.
-
Flexible data modeling: GCP Firestore’s document-oriented nature allows for flexible data modeling, meaning that you can easily adapt your data structure as your application evolves. This flexibility makes it easy to handle complex data relationships and accommodate changing business requirements.
-
High performance: GCP Firestore’s strong consistency and indexing capabilities ensure that your queries are fast and efficient. This allows for quick retrieval of data, improving the overall performance of your application.
-
Managed database service: GCP Firestore is a fully managed service, meaning that Google takes care of all the operational aspects of running the database. This includes tasks such as hardware provisioning, software updates, and data backups, allowing you to focus on building your application.
Getting Started with GCP Firestore
Creating a GCP project
To begin using GCP Firestore, you need to have a GCP project. If you don’t have one already, you can create a new project by following these steps:
- Go to the Google Cloud Console.
- Click on the project dropdown, and then click “New Project”.
- Enter a name for your project and select your desired organization. You can also choose to enable the “Billing” option if you want to associate your project with a billing account.
- Click “Create” to create your project.
Enabling Firestore in the GCP project
Once you have created your GCP project, you need to enable Firestore in that project. Follow these steps to enable Firestore:
- Go to the Google Cloud Console.
- Select your project from the project dropdown.
- In the left navigation menu, click on “Database” and then select “Firestore”.
- Click on the “Create database” button.
- Choose the location for your database. Firestore offers multiple locations to store your data, so select the location that is closest to your users or applications.
- Click “Next” and choose the mode for your database. Firestore offers two modes: Native mode and Datastore mode. Select the mode that best suits your needs.
- Click “Enable” to enable Firestore in your project.
Setting up authentication and access control
To secure your Firestore database and control access to your data, you can set up authentication and access control. Here are the steps to follow:
- Go to the Google Cloud Console.
- Select your project from the project dropdown.
- In the left navigation menu, click on “IAM & Admin” and then select “IAM”.
- Click on the “Add” button to add a new member or select an existing member to assign a role.
- Choose the desired role(s) for the member. Roles define the permissions that the member will have, such as read, write, or admin access.
- Click “Save” to apply the changes.
By configuring authentication and access control for your Firestore project, you can ensure that only authorized users or applications can access and modify your data.
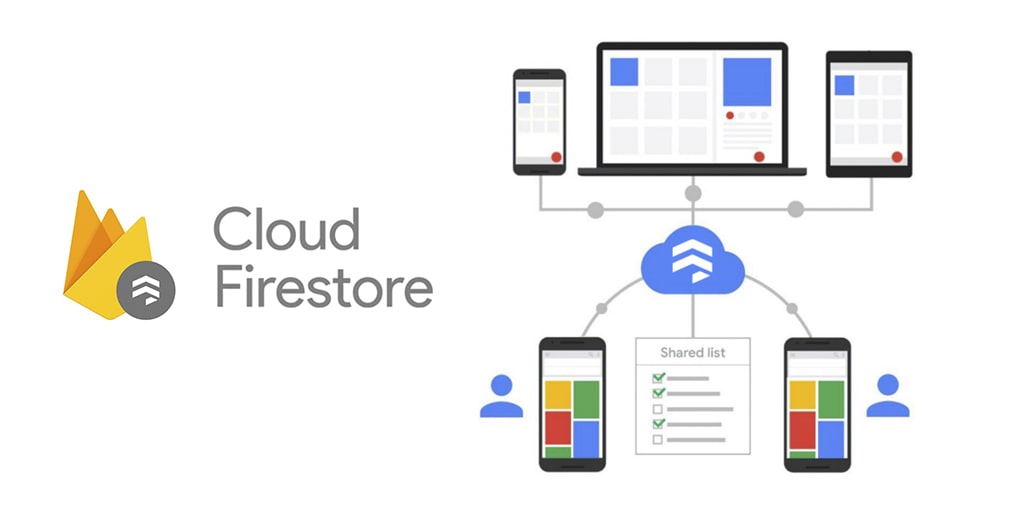
Data Modeling in GCP Firestore
Basic concepts of data modeling in Firestore
When modeling your data in Firestore, it is important to understand the basic concepts that Firestore uses. These concepts include collections, documents, and fields.
-
Collections: A collection is a group of related documents. It is similar to a table in a relational database. Collections can contain any number of documents and can be nested within other collections.
-
Documents: A document is a set of key-value pairs. It is similar to a row in a relational database. Documents must be stored within a collection and must have a unique identifier, called a document ID.
-
Fields: Fields are the individual key-value pairs within a document. Each field has a name and a value and can hold any data type supported by Firestore, such as strings, numbers, booleans, arrays, or nested objects.
Choosing the right data structure
When modeling your data in Firestore, it is important to choose the right data structure to optimize for your specific use case. Consider the following guidelines:
-
Denormalization: Firestore is designed to support denormalized data models, meaning that you can duplicate data across multiple documents to improve query performance. This allows you to query for a document and retrieve all necessary data in a single read operation, rather than having to perform multiple queries and join the data.
-
Balancing read and write operations: When designing your data structure, you should consider the balance between read and write operations. If your application requires frequent updates to a specific set of fields, you may consider storing those fields in a separate document to minimize write contention and improve write throughput.
-
Avoiding deep nesting: While Firestore allows nested collections and documents, it is generally recommended to avoid excessive nesting. Deeply nested structures can make queries more complex and less efficient. Instead, consider using a flatter structure with references or IDs to related data.
Understanding collections, documents, and fields
Collections, documents, and fields are the building blocks of data modeling in Firestore. Understanding their relationships is crucial for effective data management.
-
Collections: Collections act as containers for related documents. They provide a way to organize your data and group related documents together. For example, you might have a collection called “users” to store information about your application’s users.
-
Documents: Documents are the individual units of data in Firestore. They are stored within collections and have a unique document ID that identifies them. For example, within the “users” collection, you might have documents for each user, with each document representing a specific user and containing their profile information.
-
Fields: Fields are the individual data elements within a document. They hold the actual values of your data and can be of different data types, such as strings, numbers, booleans, arrays, or nested objects. For example, within a user document, you might have fields such as “name”, “email”, and “age”.
By understanding the relationships between collections, documents, and fields, you can effectively organize and query your data in Firestore.
Scaling Strategies in GCP Firestore
Horizontal scaling
Horizontal scaling involves distributing your workload across multiple instances or nodes. In the case of GCP Firestore, horizontal scaling can be achieved by sharding your data. By shardin