Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) is a powerful tool that provides comprehensive identity and access management solutions. In this article, we will explore the basics of Azure AD and how it can streamline your organization’s security processes. From user authentication to managing access permissions, Azure AD offers a user-friendly platform for ensuring that only authorized individuals can access your company’s resources. Join us as we uncover the key features and benefits of Azure AD, equipping you with the knowledge needed to take your organization’s security to the next level.
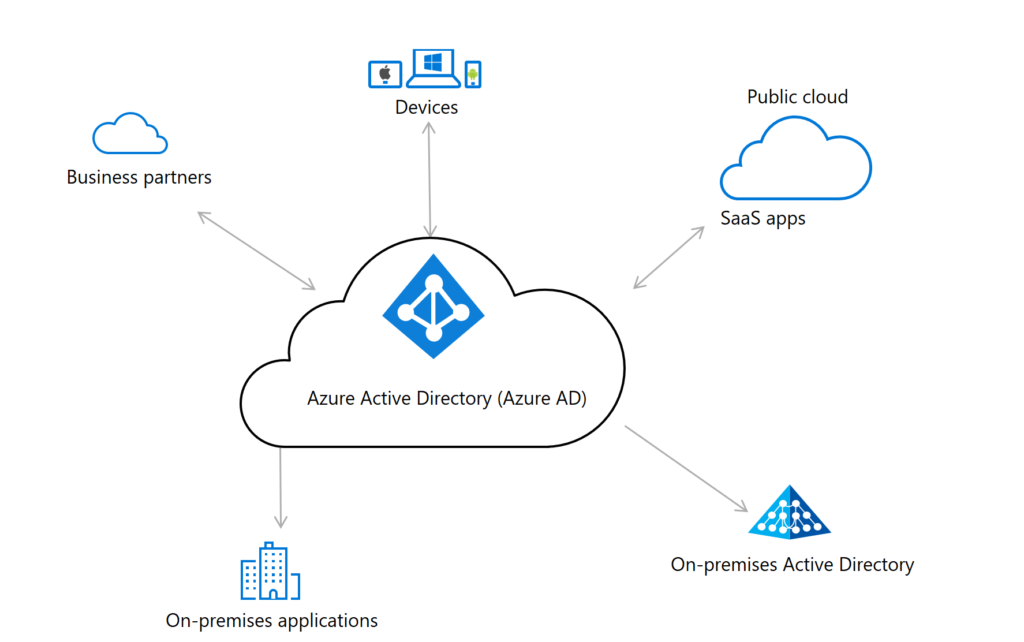
Azure Active Directory Overview
What is Azure Active Directory?
Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) is a cloud-based identity and access management service provided by Microsoft. It serves as a comprehensive solution for managing user identities and controlling access to resources in the Microsoft Azure ecosystem. Azure AD is designed to meet the needs of organizations of all sizes, providing a scalable and secure platform for managing identities, enforcing access policies, and integrating with various Azure services and applications.
Key features of Azure Active Directory
Azure AD offers a wide range of features to simplify identity and access management in the cloud. Some of the key features include:
-
User Management: Azure AD allows organizations to centrally manage user identities, create and assign user accounts, and enable self-service capabilities for users.
-
Single Sign-On (SSO): With Azure AD, users can access multiple cloud applications and services using a single set of credentials, eliminating the need for multiple passwords.
-
Multi-factor Authentication (MFA): Azure AD supports MFA, adding an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide additional validation, such as a code sent to their mobile device, in addition to their password.
-
Application Integration: Azure AD enables seamless integration with a wide range of cloud-based applications, including Microsoft 365, Salesforce, and thousands of other Software as a Service (SaaS) applications.
-
Role-based Access Control (RBAC): Azure AD provides RBAC capabilities, allowing organizations to define roles and assign permissions for accessing Azure resources, thus ensuring least privilege access.
Benefits of using Azure Active Directory
By leveraging Azure AD, organizations can enjoy several benefits in terms of identity and access management. These include:
-
Simplified administration: Azure AD streamlines the management of user identities, simplifying the provisioning and deprovisioning process, and reducing the administrative overhead.
-
Enhanced security: With features like multi-factor authentication and conditional access policies, Azure AD helps organizations strengthen their security posture and protect sensitive data.
-
Improved productivity: Single sign-on capabilities in Azure AD enhance user productivity by eliminating the need to remember multiple passwords and reducing the time spent on authentication.
-
Seamless application integration: Azure AD enables smooth integration with a wide range of applications, making it easier for users to access their resources and improving overall user experience.
-
Scalability and flexibility: Azure AD is highly scalable, allowing organizations to easily accommodate growth and adapt to changing business needs. It also offers flexibility in terms of deploying different licensing options based on specific requirements.
Architecture of Azure Active Directory
Azure AD tenants
In Azure AD, a tenant represents an organization or a partnership of organizations that shares a common instance of Azure AD. Each tenant has a unique domain name and serves as a security boundary for managing users, applications, and resources within the organization.
Within a tenant, administrators can create and manage user accounts, define access policies, and configure various security settings. Multiple tenants can be associated with a single Azure subscription, allowing organizations to manage different environments or divisions separately.
Authentication methods in Azure AD
Azure AD supports various authentication methods to verify user identities and grant access to resources. These authentication methods include:
-
Password-based authentication: Users can authenticate with Azure AD using their username and password. Azure AD enforces password complexity requirements and supports capabilities like password expiry and password writeback.
-
Multi-factor authentication (MFA): Azure AD offers MFA capabilities, allowing organizations to enable an additional factor of authentication for users, such as a phone call, text message, or mobile app verification code.
-
Federated authentication: Azure AD supports federated authentication, allowing organizations to integrate their existing on-premises Active Directory infrastructure with Azure AD. This enables users to use their existing credentials to access Azure resources without the need for separate authentication.
User roles and permissions in Azure AD
Azure AD provides a flexible role-based access control (RBAC) model for managing user roles and permissions. Administrators can define custom roles or use built-in roles to assign granular permissions to users, groups, or applications.
Some of the built-in roles in Azure AD include Global Administrator, User Administrator, Application Administrator, and many more. These roles help enforce the principle of least privilege, ensuring that users have only the necessary permissions to perform their tasks.
Integration with other Azure services
Azure AD seamlessly integrates with various Azure services, enabling organizations to extend their identity and access management capabilities. Some of the key integrations include:
-
Azure Virtual Machines: Azure AD can be used to authenticate users accessing Azure Virtual Machines, providing a secure and centralized authentication mechanism.
-
Azure App Service: Azure AD integrates with Azure App Service to enable authentication and authorization for web applications hosted on the platform, helping organizations secure their applications.
-
Azure SQL Database: With Azure AD integration, organizations can enforce authentication and authorization for accessing Azure SQL Database, ensuring that only authorized users can access the database.
-
Azure Kubernetes Service: Azure AD integration allows for managing authentication, authorization, and RBAC policies for Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) clusters, ensuring secure access to container-based applications.
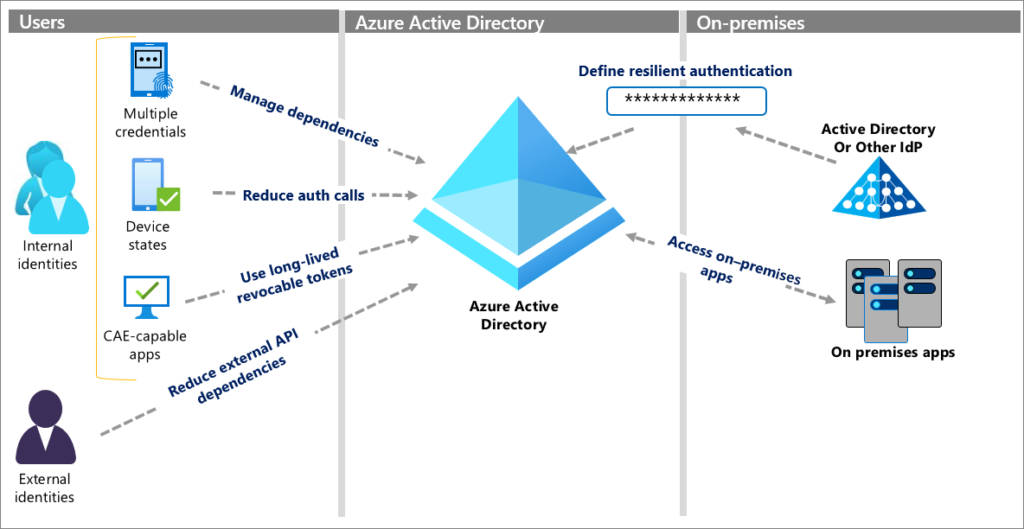
Managing User Identities in Azure Active Directory
User provisioning and deprovisioning
Azure AD simplifies the process of managing user identities by offering user provisioning and deprovisioning capabilities. Administrators can create user accounts, assign licenses, and configure user attributes using Azure AD.
When an employee joins the organization, administrators can provision a user account in Azure AD, assign the necessary licenses, and define group memberships. Similarly, when an employee leaves the organization, administrators can deprovision the user account, ensuring that the user no longer has access to company resources.
Single Sign-On (SSO)
Azure AD provides single sign-on capabilities, allowing users to sign in once and access multiple applications and resources without the need for separate authentication. With SSO enabled, users can access a wide range of SaaS applications, such as Microsoft 365, Salesforce, and others, using their Azure AD credentials.
SSO not only improves user productivity by eliminating the need for remembering multiple passwords but also enhances security by reducing the risk of password reuse or weak passwords.
Multi-factor authentication (MFA)
To enhance security, Azure AD supports multi-factor authentication (MFA), requiring users to provide additional validation when signing in to their accounts. This additional validation can be a phone call, a text message with a verification code, or approval through a mobile app.
By enforcing MFA, organizations can protect against unauthorized access even if a user’s password is compromised. MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring something the user knows (their password) and something they have (their mobile device).
Self-service password reset
Azure AD enables self-service password reset, allowing users to reset their passwords without the need for administrator intervention. In the event of forgotten passwords or account lockouts, users can verify their identities through pre-configured security questions, email verification, or authentication through a mobile app.
Self-service password reset reduces the burden on IT administrators and improves user satisfaction by providing a convenient and secure way for users to regain access to their accounts.
Controlling Access to Resources with Azure Active Directory
Azure AD application registration
Azure AD application registration allows organizations to register their applications with Azure AD, enabling them to access certain resources and APIs securely. During the registration process, organizations define the application’s name, type, and permissions required to access specific resources.
Once an application is registered, Azure AD assigns a unique client ID to the application, which can be used to authenticate and authorize the application to access the desired resources. This helps organizations ensure that only authorized applications can access their sensitive information.
Azure AD groups and group management
Azure AD groups provide a way to organize users, devices, and applications, simplifying the management of access permissions across multiple resources. Administrators can create groups and define membership rules, allowing them to easily assign permissions to a group instead of managing individual user accounts.
Azure AD supports different types of groups, including security groups, Office 365 groups, and dynamic groups. Each group type serves a specific purpose and offers unique capabilities for group management.
Role-based access control (RBAC)
Azure AD RBAC allows organizations to manage access to Azure resources based on predefined roles. Administrators can assign roles to users, groups, or applications, thus controlling the actions they can perform on specific resources.
RBAC roles in Azure AD include Owner, Contributor, Reader, and many more. Organizations can create custom roles with varying levels of granularity, ensuring that users have only the necessary permissions to perform their duties.
Conditional Access policies
Azure AD Conditional Access policies enable organizations to define and enforce access rules based on various conditions, such as user location, device compliance, and risk level. These policies allow organizations to define granular access controls tailored to their specific requirements.
By implementing Conditional Access policies, organizations can mitigate risks associated with unauthorized access attempts, enhance security, and enforce compliance requirements. Policies can be configured to require multi-factor authentication, block access from certain locations, or apply additional security measures based on the risk level of the user or device.
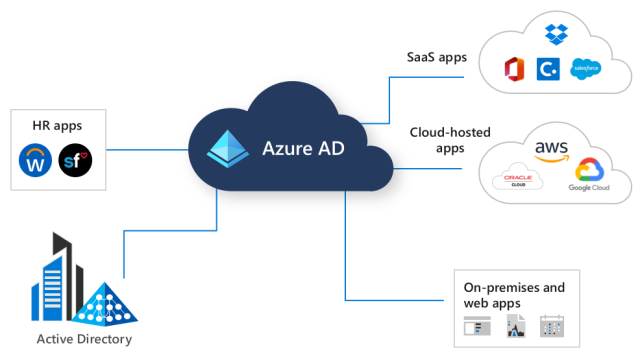
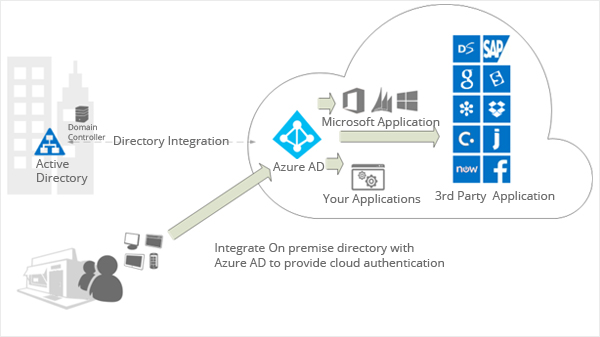
Integrating Azure Active Directory with On-Premises Active Directory
Azure AD Connect
Azure AD Connect is a tool provided by Microsoft that enables organizations to synchronize their on-premises Active Directory with Azure AD. It provides a seamless and automated way to keep user accounts, passwords, and other attributes in sync between on-premises and cloud environments.
By deploying Azure AD Connect, organizations can ensure that user identities, group memberships, and other attributes are kept up to date across both environments, enabling a consistent user experience and simplified administration.
Directory Synchronization
Directory synchronization with Azure AD allows organizations to synchronize user accounts and other directory objects from their on-premises Active Directory to Azure AD. This synchronization ensures that user accounts and attributes are consistent between on-premises and cloud environments.
Azure AD supports different synchronization modes, such as password hash synchronization and pass-through authentication. These modes allow for seamless authentication and enable users to access cloud resources using their on-premises credentials.
Password Hash Synchronization
Azure AD Password Hash Synchronization (PHS) is a feature of Azure AD Connect that enables organizations to synchronize password hashes from their on-premises Active Directory to Azure AD. This allows users to sign in to Azure AD and access cloud resources using their on-premises passwords.
With password hash synchronization, organizations can benefit from a seamless sign-on experience for users, eliminating the need for users to remember multiple passwords for on-premises and cloud environments.
Pass-through Authentication
Azure AD Pass-through Authentication (PTA) is another authentication method provided by Azure AD Connect. With PTA, user passwords are validated against the on-premises Active Directory, eliminating the need to synchronize password hashes to the cloud.
Pass-through Authentication provides a secure and convenient way to authenticate users against their on-premises Active Directory, while still benefiting from the cloud-based identity and access management capabilities of Azure AD.
Securing Your Azure Active Directory
Azure AD Identity Protection
Azure AD Identity Protection is a feature that helps organizations detect and mitigate identity-related risks in real-time. It uses machine learning algorithms to analyze user behavior and sign-in patterns, detecting anomalies and suspicious activities.
By leveraging Azure AD Identity Protection, organizations can proactively identify and respond to potential identity-related threats, such as account takeovers, brute-force attacks, and risky sign-in attempts. This helps enhance the overall security posture of the organization.
Azure AD Privileged Identity Management (PIM)
Azure AD Privileged Identity Management (PIM) provides a way to control and manage privileged access to critical resources in Azure AD. It allows organizations to assign time-limited, just-in-time administrative access to users who need it, reducing the risk of unauthorized access and privilege abuse.
With PIM, organizations can enforce approval workflows, monitor privileged access activity, and provide users with elevated access only when needed. This helps maintain a least privilege access model and improves overall security.
Auditing and logging
Azure AD provides comprehensive auditing and logging capabilities, allowing organizations to track and monitor user activities, permission changes, and other security-related events. These logs can be used for compliance purposes, troubleshooting, and detecting potential security breaches.
By reviewing audit logs, organizations can gain insights into user activities and detect any unusual or suspicious behavior. This helps organizations maintain visibility into their Azure AD environment and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
Threat detection and monitoring
Azure AD offers built-in threat detection and monitoring capabilities to identify security threats and potential attacks targeting user identities. It leverages machine learning algorithms and anomaly detection techniques to identify security risks.
When a security threat or suspicious activity is detected, Azure AD can send notifications or trigger automated actions to address the threat. This helps organizations stay ahead of potential attacks and take proactive measures to protect their Azure AD environment.
Azure Active Directory Use Cases
Enterprise application access management
Azure AD provides a centralized identity and access management platform for enterprise applications. It allows organizations to enable single sign-on (SSO) for applications, enforce multi-factor authentication (MFA), and manage user access permissions.
By leveraging Azure AD, organizations can simplify the onboarding and offboarding processes for applications, streamline user access management, and enhance overall security for enterprise applications.
Cloud-native application authentication and authorization
Azure AD offers robust authentication and authorization capabilities for cloud-native applications built on Azure. Through Azure AD application registration, developers can integrate their applications with Azure AD for secure user authentication and authorization.
With Azure AD, developers can leverage features such as OAuth 2.0 and OpenID Connect to authenticate users, obtain access tokens, and enforce fine-grained access control policies specific to their applications.
B2B and B2C collaboration
Azure AD enables organizations to collaborate securely with external partners, customers, and suppliers through its business-to-business (B2B) and business-to-consumer (B2C) capabilities.
With B2B collaboration, organizations can invite external users to access specified resources using their own Azure AD or social media accounts. B2C collaboration, on the other hand, enables organizations to provide a seamless sign-up and sign-in experience to customers using their preferred social media or email accounts.
Azure AD integration with SaaS applications
Azure AD integrates seamlessly with thousands of Software as a Service (SaaS) applications, providing a unified identity management solution for both Microsoft and third-party applications.
By integrating with Azure AD, organizations can enforce consistent authentication and access control policies for SaaS applications, streamlining user onboarding and offboarding processes, and improving overall security and user experience.
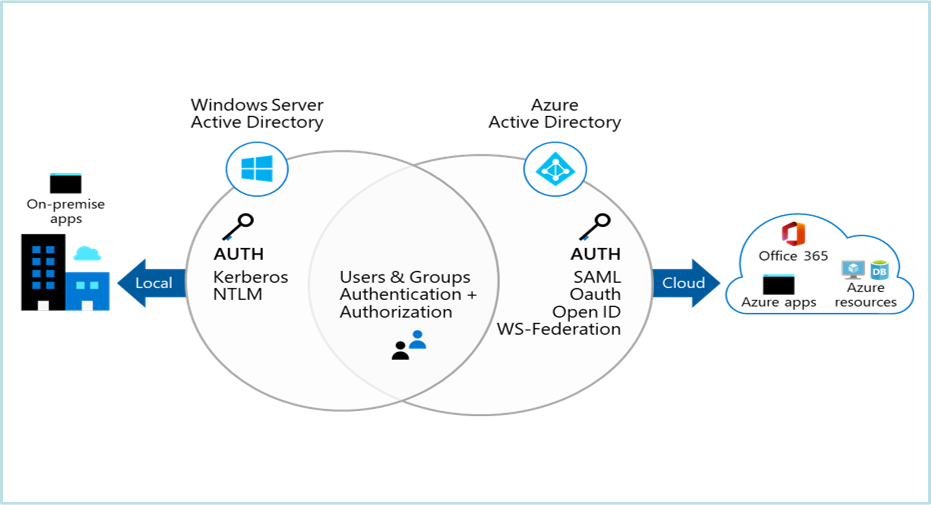
Azure Active Directory vs. Active Directory Domain Services
Differences between Azure AD and AD DS
Azure AD and Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) serve different purposes and cater to different scenarios:
-
Azure AD: Azure AD is a cloud-based identity and access management service designed for managing identities and securing access to resources in the Azure ecosystem. It is primarily used for cloud-based scenarios and does not provide the same level of control and management capabilities as on-premises AD DS.
-
AD DS: AD DS is the on-premises counterpart of Azure AD, providing a comprehensive directory service for managing identities, group policies, and domain-based authentication. AD DS is typically used in traditional on-premises environments and offers extensive control over user management, domain services, and group policies.
Use cases for Azure AD vs. AD DS
The choice between Azure AD and AD DS depends on the specific use case and requirements:
-
Cloud-centric scenarios: Azure AD is the preferred choice for organizations that rely predominantly on cloud-based applications and resources. It provides seamless integration with Azure services, offers SSO capabilities for SaaS applications, and simplifies identity management in the cloud.
-
Hybrid scenarios: Organizations that have a combination of on-premises and cloud environments can leverage Azure AD Connect to synchronize user accounts and passwords between on-premises AD DS and Azure AD. This allows for a hybrid identity solution, enabling users to seamlessly access resources in both environments.
-
Traditional on-premises environments: AD DS is the preferred choice for organizations that require comprehensive control and management over their on-premises identities, group policies, and domain services. AD DS offers extensive features and flexibility for managing user accounts and access controls in traditional on-premises environments.
Hybrid scenarios and co-existence
For organizations with both on-premises and cloud environments, Azure AD and AD DS can coexist and be used together in hybrid scenarios. Azure AD Connect enables the synchronization of user accounts and passwords between the two environments, providing a seamless sign-on experience for users.
With this hybrid setup, organizations can leverage the benefits of both Azure AD and AD DS. Users can authenticate against their on-premises AD DS while still accessing cloud resources with their Azure AD credentials. This allows for a gradual migration to the cloud while maintaining compatibility with existing on-premises infrastructure.
Azure Active Directory Pricing and Licensing
Azure AD editions and pricing
Azure AD offers different editions to cater to various organizational needs:
-
Azure AD Free: A no-cost edition of Azure AD that provides basic identity and access management capabilities, including user and group management, self-service password reset, and single sign-on for Azure AD-integrated applications.
-
Azure AD Premium P1: This edition includes all the features of Azure AD Free, along with advanced security and identity protection capabilities. It offers features like Conditional Access policies, Azure AD Identity Protection, Privileged Identity Management, and self-service group management.
-
Azure AD Premium P2: This is the most comprehensive edition of Azure AD, offering all the features of Azure AD Premium P1, along with additional advanced identity and security features. It includes capabilities like Identity Governance, Identity and Access Management for SaaS apps, and Privileged Identity Management for Azure resources.
The pricing for each edition can be found on the official Azure pricing page.
Licensing options for Azure AD
Azure AD offers different licensing options to accommodate various organizational needs:
-
User-based licensing: Organizations can license Azure AD on a per-user basis, providing each user with access to the required Azure AD features. This licensing model allows organizations to scale their licensing based on the number of users who require Azure AD capabilities.
-
Enterprise Agreement (EA): Organizations with an EA can include Azure AD licensing as part of their agreement, providing simplified management and billing for Azure AD deployment across their enterprise.
-
Microsoft 365 and Office 365 SKUs: Azure AD features are included in various Microsoft 365 and Office 365 SKUs. Organizations can choose the appropriate licensing plan that meets their requirements, and the Azure AD features will be included as part of the overall subscription.
Azure AD Free vs. Azure AD Premium
The choice between Azure AD Free and Azure AD Premium depends on the specific needs and requirements of the organization:
-
Azure AD Free: Azure AD Free is suitable for organizations that require basic identity management capabilities, such as user and group management, single sign-on for Azure AD-integrated applications, and self-service password reset. It is a cost-effective option for small businesses or organizations with limited identity management requirements.
-
Azure AD Premium: Azure AD Premium is recommended for organizations that require advanced security, identity protection, and governance capabilities. It offers features like Conditional Access policies, Azure AD Identity Protection, Privileged Identity Management, and self-service group management. Azure AD Premium is suitable for organizations with complex identity management needs, compliance requirements, or those seeking enhanced security features.
Conclusion
Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) is a powerful cloud-based identity and access management service offered by Microsoft. It provides a comprehensive solution for managing user identities, enforcing access policies, and integrating with various Azure services.
Key features of Azure AD include user management, single sign-on (SSO), multi-factor authentication (MFA), and application integration. By leveraging Azure AD, organizations can simplify administration, enhance security, improve productivity, and achieve scalability and flexibility.
Azure AD offers various capabilities for managing user identities, controlling access to resources, and securing the Azure AD environment. These include provisions for user provisioning and deprovisioning, single sign-on (SSO), multi-factor authentication (MFA), and self-service password reset.
Controlling access to resources is made easier with Azure AD through features like application registration, group management, role-based access control (RBAC), and conditional access policies.
Organizations can seamlessly integrate Azure AD with their on-premises Active Directory using Azure AD Connect, enabling directory synchronization, password hash synchronization, and pass-through authentication.
To ensure the security of Azure AD, features like Azure AD Identity Protection, Azure AD Privileged Identity Management (PIM), auditing and logging, and threat detection and monitoring are available.
Azure AD has a wide range of use cases, including enterprise application access management, cloud-native application authentication and authorization, B2B and B2C collaboration, and integration with SaaS applications.
Understanding the differences between Azure AD and Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) is crucial. While Azure AD is designed for cloud-based scenarios, AD DS serves traditional on-premises environments. Hybrid scenarios and co-existence are possible through solutions like Azure AD Connect.
Azure AD offers different editions, including Azure AD Free, Azure AD Premium P1, and Azure AD Premium P2, each with its own set of features and pricing. Organizations can also choose the appropriate licensing options based on their needs.
In conclusion, Azure Active Directory provides organizations with a robust and scalable solution for managing user identities and controlling access to resources in the cloud. By leveraging the capabilities of Azure AD, organizations can enhance security, simplify administration, and improve overall productivity.
