Alright, folks, today we’re tackling a crucial topic that affects not only the healthcare industry but also our personal well-being – healthcare data security on GCP. With the rapid advancements in technology and the increasing reliance on cloud services, it’s vital to ensure that our sensitive medical information is safeguarded. In this article, we’re going to delve into the world of GCP for healthcare, exploring the importance of compliance and data security. So, grab a coffee, sit back, and let’s dive into the world of ensuring healthcare data security on GCP.
GCP for Healthcare: Compliance and Data Security
As we delve into the world of healthcare data management, it is crucial to ensure compliance and data security. Google Cloud Platform (GCP) offers a robust and reliable solution for healthcare organizations, enabling them to meet regulatory requirements and protect sensitive patient information. In this article, we will explore the importance of data security in healthcare, the compliance and regulatory requirements in this industry, and highlight key principles for healthcare data security on GCP.
Overview of GCP
Introduction to Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
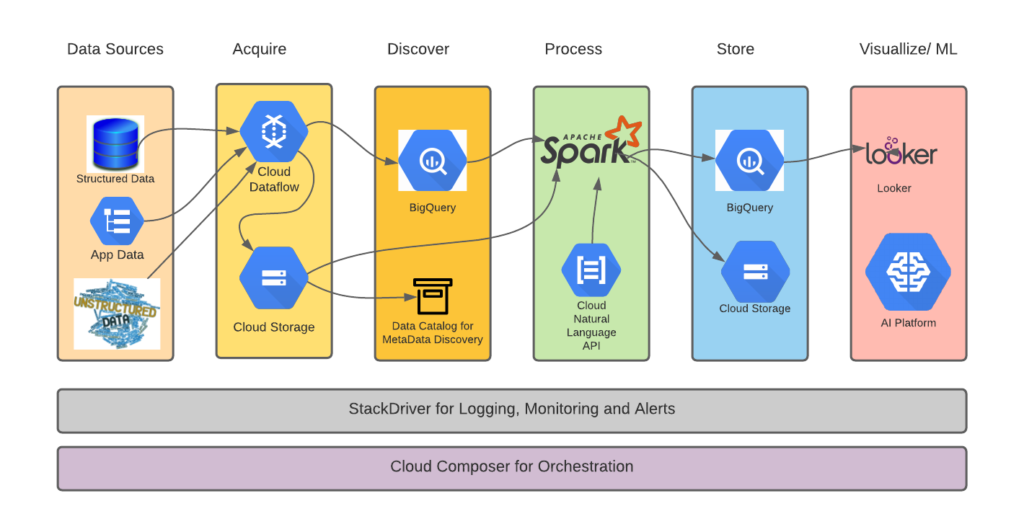
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) is a comprehensive suite of cloud computing services provided by Google. It offers a wide range of features and capabilities that empower businesses to build, deploy, and manage applications and data on the cloud. GCP provides the scalability, reliability, and performance needed for healthcare organizations to efficiently manage their data and applications.
Features and Capabilities of GCP
GCP offers a myriad of features and capabilities that make it a preferred choice for healthcare data management. These include secure and scalable storage solutions, advanced data analytics tools, machine learning capabilities, and robust security measures. GCP is built on Google’s global infrastructure, ensuring high availability and disaster recovery capabilities.
Advantages of Using GCP for Healthcare Data Management
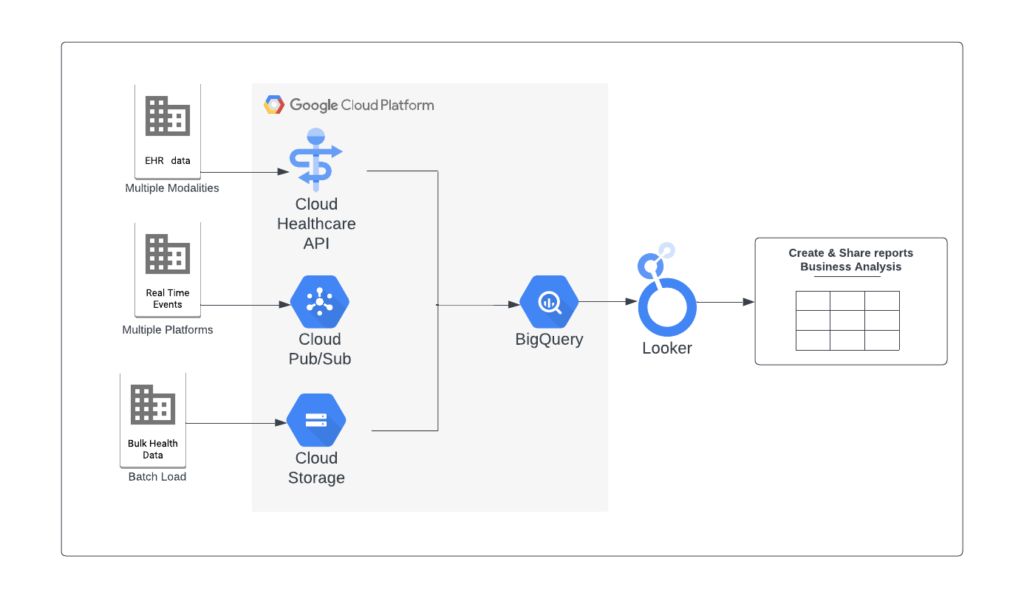
The adoption of GCP in the healthcare industry brings numerous advantages. GCP’s scalable infrastructure allows healthcare organizations to handle large volumes of data securely and efficiently. The platform offers advanced encryption methods, access controls, and secure storage solutions to protect sensitive patient information. GCP also provides compliance certifications, such as HIPAA, which ensures that the platform adheres to industry-standard security and privacy requirements.
Importance of Data Security in Healthcare
Understanding the Sensitivity of Healthcare Data
Healthcare data is highly sensitive and confidential, consisting of personal medical records, diagnoses, treatment plans, and other private information. This sensitive data must be protected to maintain patient trust and comply with legal obligations. Breaches in healthcare data can have severe consequences, ranging from financial loss to reputational damage and even potential harm to patients.
Potential Risks and Consequences of Data Breaches
Data breaches in healthcare can result in various negative outcomes. When patient information falls into the wrong hands, it can be exploited for identity theft, insurance fraud, or other malicious activities. Moreover, healthcare organizations that experience data breaches may face legal penalties, regulatory investigations, and class-action lawsuits. The reputational damage caused by a breach can erode patient trust and undermine the confidence of stakeholders.
Significance of Protecting Patient Privacy
Protecting patient privacy is not only an ethical responsibility but also a legal requirement. Patients entrust healthcare providers with their most intimate and personal information, and it is imperative that this information remains secure and confidential. By implementing robust data security measures, healthcare organizations can ensure patient privacy and maintain the trust and loyalty of individuals seeking care.
Compliance and Regulatory Requirements
Overview of HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act)
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) is a crucial legal framework that governs the protection of patient data in the United States. HIPAA establishes regulations and standards for the security, privacy, and confidentiality of individually identifiable health information, also known as protected health information (PHI). Compliance with HIPAA is mandatory for healthcare providers, health plans, and healthcare clearinghouses.
HIPAA Security Rule and its Impact on Healthcare Data Security
The HIPAA Security Rule specifically addresses the security requirements for protecting PHI. It mandates the implementation of administrative, physical, and technical safeguards to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of electronic protected health information (ePHI). These safeguards include access controls, encryption, audit controls, and employee training. GCP provides the necessary security measures to help healthcare organizations comply with the HIPAA Security Rule.
Other Relevant Compliance Standards and Regulations
In addition to HIPAA, healthcare organizations must comply with other relevant compliance standards and regulations, depending on their geographical location and the nature of their operations. Some notable examples include the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union, the Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act (HITECH Act) in the United States, and the Information Standard for the NHS in the United Kingdom. GCP offers features and functionalities to assist healthcare organizations in meeting these diverse compliance requirements.

Key Principles for Healthcare Data Security on GCP
To ensure robust data security on GCP, healthcare organizations should adhere to key principles and best practices. By implementing these principles, organizations can protect patient privacy, maintain regulatory compliance, and mitigate the risk of data breaches.
Data Encryption and Access Controls
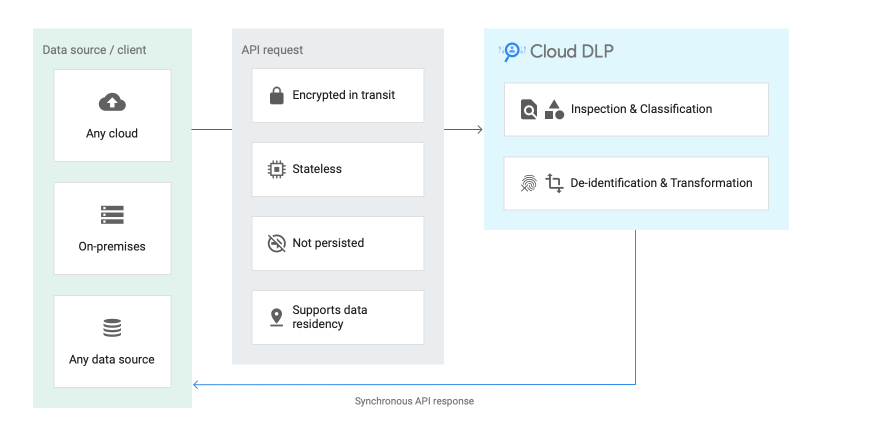
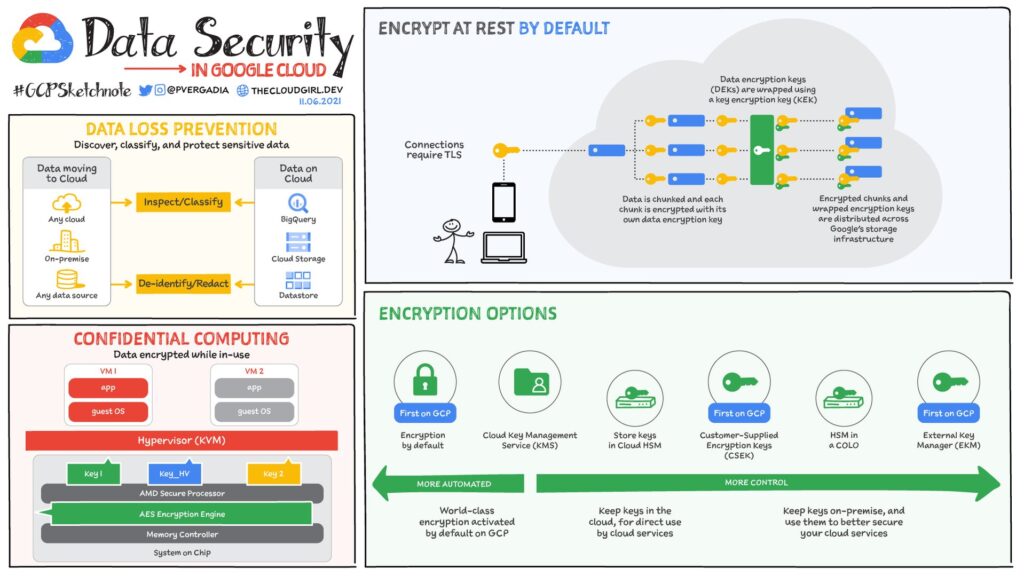
Data encryption is a fundamental aspect of healthcare data security. GCP provides various encryption methods to protect data at rest and in transit. Healthcare organizations should implement encryption to safeguard sensitive information. Additionally, access controls, such as user permissions and role-based access control (RBAC), should be enforced to restrict data access only to authorized individuals.
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Identity and Access Management (IAM) plays a vital role in healthcare data security. Healthcare organizations should implement IAM practices that include robust authentication mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), to verify the identity of users accessing patient information. Audit logs and access monitoring should be implemented to track and investigate any unauthorized access attempts.
Secure Storage and Data Management
Choosing appropriate storage solutions on GCP is crucial for healthcare organizations. GCP provides secure and scalable cloud storage options that comply with regulatory requirements. Healthcare organizations should leverage these solutions to securely store and manage patient data, ensuring data backups and replication for disaster recovery purposes. Proper data lifecycle management should also be implemented to retain and dispose of data as required by regulations.
Regular Auditing and Monitoring
Continuous auditing and monitoring are essential for healthcare data security on GCP. By implementing security information and event management (SIEM) tools, healthcare organizations can gain real-time visibility into potential security threats and vulnerabilities. Regular log management and analysis help identify and respond to security incidents promptly.
Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity
Disaster recovery and business continuity planning are critical for healthcare organizations that rely on GCP. Adequate backup and replication strategies should be in place to ensure that patient data is recoverable in the event of a disaster. Periodic testing of disaster recovery plans is crucial to validate their effectiveness.
Employee Training and Education
Effective employee training and education programs are essential for healthcare data security. Healthcare organizations should provide comprehensive security awareness training to employees, ensuring they understand their role in protecting patient data and complying with security policies and procedures. Regular training sessions help reinforce good security practices and keep employees informed about emerging threats.
Incident Response and Incident Management
The ability to promptly respond to and manage security incidents is critical for healthcare organizations on GCP. Incident response plans and procedures should be established to ensure a swift and effective response in the event of a breach. Healthcare organizations should conduct drills and exercises to test the effectiveness of their incident response plans.
Vendor Management and Third-Party Assessments
Healthcare organizations often rely on vendors and third-party service providers for various services. When partnering with vendors, it is essential to conduct thorough security assessments to evaluate their security practices. Vendors should adhere to strict security requirements, adequately protect patient data, and comply with relevant regulations. Regular monitoring and auditing of vendors should be conducted to ensure ongoing compliance.
In conclusion, GCP offers healthcare organizations a comprehensive platform for compliance and data security. By understanding the sensitivity of healthcare data, complying with regulatory requirements, and implementing key principles for data security, healthcare organizations can confidently leverage GCP to manage their data securely. As technology continues to advance and threats evolve, healthcare organizations must remain vigilant and prioritize robust data security measures to protect patient privacy and maintain the trust of individuals seeking care.
